Connect Cells and Support Body Structure
Collagen in the human body is present in all tissues, widely distributed in the skin, bones, eyes, teeth, tendons, internal organs, and other parts. As a major component of the extracellular matrix, it connects cells and supports the body's structure, accounting for approximately 30% of the total protein in the human body. In the skin, collagen makes up over 70% of the protein content.
Collagen exhibits a triple-helix structure, formed by three amino acid chains twisted together. Each amino acid chain is primarily composed of repeating sequences of glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, interspersed with other types of amino acids. To date, nearly 30 types of collagen have been discovered in the human body, named sequentially as Type I, Type II, Type III, and so on. Different types of collagen vary in their locations, structures, and functions.
Maintain Health and Beauty; Maintain Vitality
When tissues are rich in collagen, the body's bones and joints are strong and resilient, the skin is hydrated and elastic, and even nails and hair radiate a healthy glow.
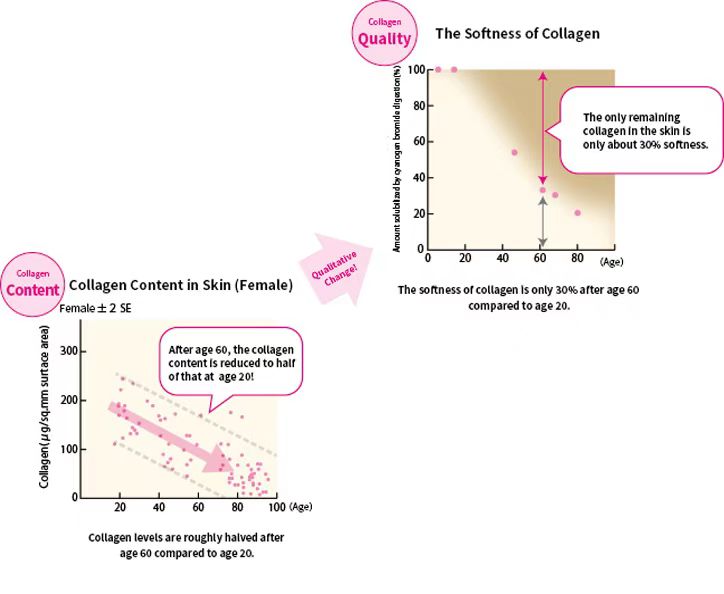
To sustain health, beauty, and vitality, collagen is indispensable. However, as we age, not only does collagen gradually diminish, but the remaining collagen in the body also loses its flexibility. Aging is accompanied by the loss and degradation of collagen. Proper supplementation of collagen can significantly benefit bodily functions, help maintain health and beauty, and delay the signs of aging.
Collagen and its hydrolyzates have similar structure with human skin collagen and have good compatibility. They can enter deep layers of human skin and present good nutritional effect. In addition, collagen contains a large number of amino acids such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine, as well as abundant natural moisturizing factors such as glycine, which can improve the water storage capacity of tissue cells and have a good moisturizing effect. Many collagen peptides are related to the growth, division, proliferation, migration and differentiation of skin cells, which can provide nutrients to the skin, delay skin aging, and promote skin wound repair. Collagen solution also has a strong anti-radiation effect. Collagen has been widely used in the field of cosmetics.
Moisturizing Retention
Collagen is a moisturizing ingredient that keeps the skin moisturizing. When moisturizing the stratum corneum, it also repairs the dry and damaged skin and helps maintain the best moisturizing state.
Collagen added in cosmetics has different moisturizing mechanisms according to its type, molecular weight, source, and shape, and all of them can effectively keep the skin moisturizing and are reliable ingredients that give skin a sense of moisture and elasticity.
In cosmetics, collagen is mainly added in the form of water-soluble collagen, hydrolyzed collagen, and collagen peptides. Generally speaking, the larger the molecular weight of the collagen added, the better the moisturizing performance is; the smaller the collagen molecular weight is, the better the penetrating and nourishing effect produced. By adding collagen of different molecular weights in a specified proportion, the cosmetics can obtain multiple moisturizing effects, and can present better repair and moisturizing function on the skin.
Repairability
Collagen is similar to the collagen structure in the skin, with excellent biological properties, and is well absorbed by skin. Collagen can promote the proliferation and repair of epithelial cells, and supplement the amino acids needed by the skin, which can fill and repair damaged and aging skin.
Nutritive
Collagen can enter deep layers of skin, give skin necessary nutrients (amino acids), maintain the stability and integrity of the collagen fiber structure, enhance the activity of collagen in the skin, and improve the living environment of skin cells. It can also promote the metabolism of tissues, so as to achieve the effect of nourishing and moisturizing of skin and hair.
Anti-wrinkle
The similarity between the structure of collagen and the structure of the stratum corneum of skin determines its good compatibility, affinity and permeability with skin. It can penetrate into the epidermis of skin to be fully absorbed, and form a very thin layer over skin surface. Thus, the skin is plump and wrinkles are stretched, with the increased skin density, skin tension can be generated, which further produces the anti-wrinkle effect.
Whitening
The tyrosine residues in collagen compete with tyrosine in the skin and bind to the active center of tyrosinase, inhibiting tyrosinase catalyzing the conversion of tyrosine to dopa, which prevents the formation of melanin in the skin, so as to achieve the whitening effect.


